Vaping Addictions Signify Larger Issues
Today, vaping has become an unavoidable topic of discussion. Fordham University’s Health Services even has a sign listing ten things to know about vaping outside their door. This attention has largely resulted from the recent emergence of vaping-related illnesses and deaths.
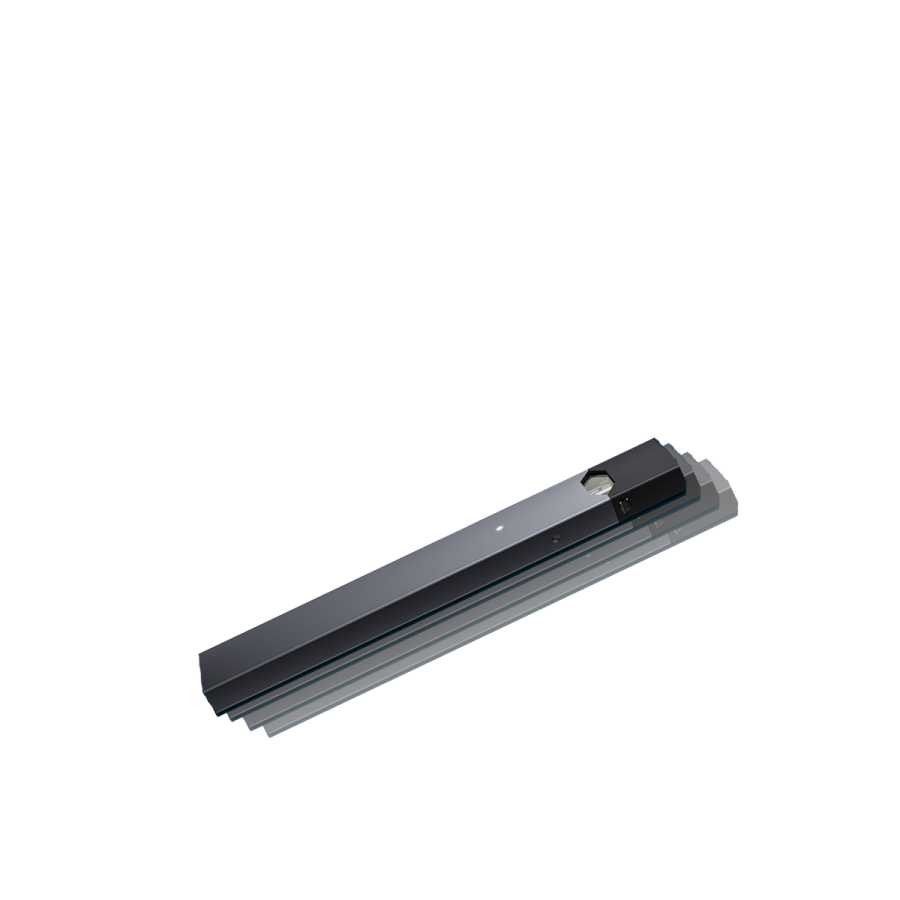
“Vaping” refers to the use of electronic cigarettes or other similar devices, which typically contain nicotine but can be used to smoke different chemicals like THC. One of the reasons that vaping has become a cause of concern is because of its popularity among young students in high school and college. Nicotine devices have become a serious source of addiction for a young population that was projected to be the generation that would end cigarette smoking for good. The long-term effects of using these devices remain unknown. For now, though, it is crucial to investigate its appeal.
According to a study by the University of Michigan, the number of college students vaping either nicotine or marijuana is on the rise. College has always been a notorious environment for peer pressure and substance abuse, where students can often be reckless, especially in freshman year, at the beginning of their time at university. Peer validation is a big motivation to engage in potentially dangerous behavior with drugs or alcohol.
Vaping is different, though — it is oftentimes a near-constant habit. Vaping devices, especially small ones like those of the popular JUUL brand, are easily concealable and can be carried around constantly. It’s instant satisfaction accessible at practically any time, unlike alcohol, which is generally limited to parties on the weekends.
Another reason many students say they vape is to manage symptoms of declining mental health, which are often compounded by stress and peer pressure. It is no secret that increasing amounts of college students struggle with anxiety, and that is likely a prominent reason that their population is among the highest proportion of vape users. Nicotine can become a coping mechanism for the stressful environment of college.
Teenagers are often thought to have a sort of tunnel vision, unable to see the consequences of their actions. Although college students tend to grow out of this by the time they graduate, many vape addictions start freshman year when students are new to the environment. The feeling of invincibility that often accompanies youth can blind them from the concerning facts. Vaping’s long-term effects are largely unknown so far. Until recently, most young vape users didn’t see a downside to the practice. Users are often okay with taking potential risks because it is presented in a seemingly safe social setting and is popular among peers.
Social motivation plays a critical role because teens often first vape in a social environment. Soon, though, they find themselves unexpectedly addicted. Unlike alcohol, it is incredibly easy to become addicted to nicotine after a small number of uses. What starts as a quick moment of experimentation can escalate into something much more significant.
Quitting is not only difficult due to the addictive properties of nicotine. Often, the roots of the problem are those that the students are attempting to cope with, and which need to be addressed adequately. Vaping becomes just another symptom of a much more significant problem.
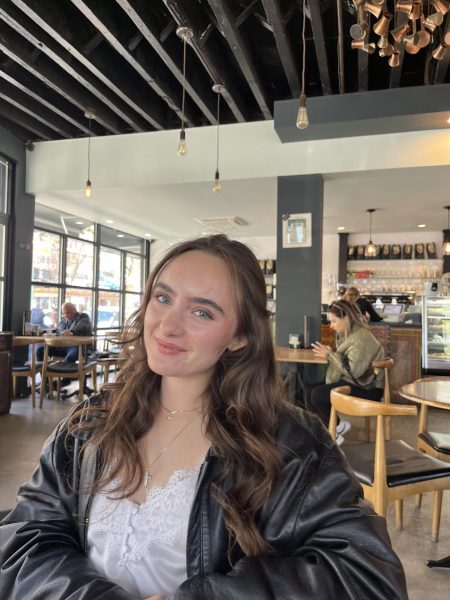
One Fordham student cited mental health as her primary reasoning for beginning vaping her freshman year. She was able to improve her mental health but still struggles with an addiction to vaping. She explains, “Vaping, for me, is still tied to sad memories. It is still something that used to be a crutch.”
A habit that started as a means of social strategy and acclimating to the difficulties of college spirals into something incredibly difficult to escape. Young adults should not be shamed for their experiences, but instead, supported. We need to discuss the motivations for their behavior. College students, who often use e-cigarettes and vapes prior to smoking in the first place, use the devices for reasons that reflect broader issues.
The widespread popularity of vaping will hopefully become another reason to promote and improve college mental health resources. While efforts should certainly be made to protect students from the harmful effects of vaping, young adults need to be encouraged to employ healthy methods of coping with anxiety and other adverse mental health symptoms.
Columnist volume 101, Editorial Director and Opinion Editor volume 102